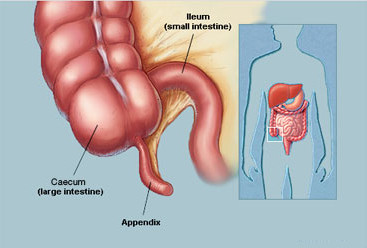
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix. Appendix is the finger like structure originated from the cecum part of ascending colon.
Appendix functions-
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix . Appendix play an important role in storing good bacteria in the GI tract after a diarrhea and illness and help to maintain gut flora.
Causes-
1. Obstructions- Fecolith ( term used for calcified and obstruction and lead to rupture ) which cause perforation , Abscess formation peritonitis.
2. Parasites , foreign bodies , swollen lymph nodes in lining of appendix.
3. Trauma and injuries.
Pathophysiology-
1. Blockage in the lumen of appendix leads to increase pressure inside the appendix because of increase amount of mucous from mucosal lining and increase fluid along with Increased bacteria. These bacteria are already present in appendix which maintain flora. These bacteria can go anywhere and increase again pressure so within 48-72 hrs patient have risk of perforation.
2. When Increased pressure cause major venous obstruction ( occlusion of the blood flow) and blood remain stagnant which leads to clot formation and cause ischemia to appendix ( diminished blood supply to appendix) which cause slow breakdown of walls of appendix.
3. These all conditions lead to the peritonitis and which leads to septic shock and death.
Sign and symptoms-
1. Abdominal pain which is dull around the belly button and radiate right Lower quadrant also called mecburney's point.
2. Poor appetite.
3. Elevated temperature.
4. Nausea and vomiting.
5. Desire to be in lie in fetal position which give relief in pain.
6. Increased wBCs and infection.
7. Inability to pass gas , stool and may have constipation and diarrhea.
8. Experience rebound tenderness i.e. when press there will be no pain but when left pressure there is too much pain.
9. Abdominal rigidity.
Treatment-
Surgeries-
1. Appendectomy - Removal of Appendix.
2. Laparotomy - surgical opening made in abdomen to treat and diagnose many diseases.
3. Laproscopic surgeries- A vedio camera with tube is inserted in small cut on body to repair and remove tissues.
Medications-
Generally antibiotics are given to patient to overcome the infection and reduce infection.
Patient care-
Pre- op ( before operation)-
1. Vital signs monitor.
2. Monitor sign of peritonitis and perforation.
Perforation-
In this case patient have relief of pain with Increased level of pain. If pain get relief after the sever pain it will indicate that appendix may have rupture and all content get release into the abdomen. Which leads to the peritonitis and cause.
- Increase heart rate.
- Increase pulse rate.
- Increase temperature.
- Pain relief with fetal position.
3. Do not provide hot applications on stomach to pain relief because it can lead to rupture of appendix.
4. Do not use enema and laxatives because it can lead to rupture of appendix.
Post op care ( after operation )-
1. Monitor vital sign.
2. Monitor site for infection.
3. Care for drain as per doctor ordered.
4. Positioning should provide to the patient to remove drainage.
5. Ambulate patient which help to come out all waste fluid easily into drain.
6. Provide spirometry , coughing and deep breathing exercises.
7. Administer IV antibiotics as per ordered.
8. Administer pain medications as per ordered.
9. Monitor bowel sound and should present 2- 3 days after surgery.
10. Also flatus should pass within 2 days.



No comments:
Post a Comment