It is a type of inflammaory bowel disease that cause inflammation ulcers formation in the GI tract . Another type of inflammaory bowel disease is ulcerative colitis.
Some common facts about the disease-
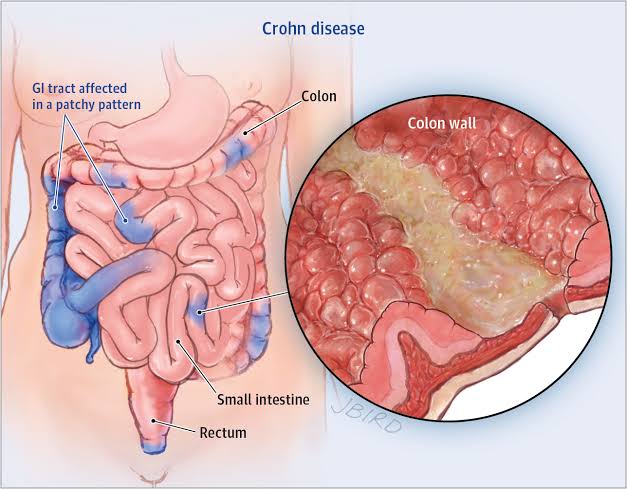
1. This disease can be found in both large and small intestine but ulcerative colitis occur in only large intestine.
2. It most likely found in the terminal of ileum and starts from the colon.
3. This disease affect all lining of the bowel and ulcerative colitis only effect the inner lining of the bowel it cause more complications.
4. Diseases found in scattered patches of infected lines after healthy lines this called cobble stone appearance.
5. Causes of diseases are unknown and most commonly caused by the faulty immune system and may be triggers by the genes.
6. This diseases have periods of flare up and remission.
7. There is no care and no colostomy and ileostomies because all parts of small and large intestine are affected. Only bowel resection , medication and diet can prevent this.
Types -
Ileocolitits - inflammation found in ileum colon.
Gastroduodenal- ulcers found in part of colon of stomach and duodenum.
Jejuno ileitis - found in jejunum.
Ileitis- ulcers found in the ileum.
Granulomatous colitis - this is only found in the colon.
Causes-
Causes are unknown but it is mainly caused by immunodeficiency , genetic and environmental factors.
Complications-
1. Abscessing fistulas - it forms sepsis. Abscessing packets of infection form within the intestine wall. Fistulas ulcers and abscess form deep in intestine wall creating an opening channel and passage of infection between intestine to intestine , intestine to organ and other skin surface.
Entro enteric- intestine to intestine abscess formations.
Perianal - due to anal abscess.
Entro vesical - abscess form Intestine to bladder.
Entrovaginal - abscess form intestine to vagina
Entro-cutaneous - abscess form intestine to skin surfaces.
2. Malnaurisment-
Small intestine get infalmed and all enzymes required for digestion of food not secret and cause malnaurisment.
3. Anal tear and fissures is complication.
4. strictures-
obstructions is common complications major narrowing of intestinal wall due to chronic inflammation which leads to scarring and limit flow of GI contents , food get stuck and cause obstructions.
5. Other complications will the arthritis , stress in gall bladder , skin rashes and eyes issues.
Sign and symptoms-
1. Abdominal pain and mainly in the right Lower side because it mainly effect ileum and that part is present in the right Lower side.
2. Ulcers in mouth and GI tract.
3. Diarrhea may be with pus , blood and mucous.
4. Loss of weight , malnaurisment and electrolyte imbalance.
5. Fissure Anal that bleed .
6. Bloating.
Treatment-
Medications-
NSAIDS - decrease pain decrease inflammation and fever.
Ant inflammatory - prevent swelling in tissues
Ant inflammatory - prevent swelling in tissues
Immuno suppressors- reduce immune response.
Steroids - modifies and stimulate hormonal effect.
Analgesic - relief pain.
Steroids - modifies and stimulate hormonal effect.
Analgesic - relief pain.
Surgery-
Colostomy - surgical creation of abdominal opening In large intestine where stool can leave.
Ileostomy- surgical connecting of small intestine to opening in abdomen so stool can leave to it.
Proto colectomy- surgical removal of rectum and all part of colon.
Colectomy- surgical removal of all part of colon.
Iv fliud therapy-
Administration of Iv fluids done to recover electrolyte imbalance.Enema may be administer to increase bowel movement and clear out stool .
Patient Care-
Goal -
Help patient to understand diet medications , surgeries .
1. Advice for smoke cessation.
2. In severe cases have to give rest for bowel and maintain NPO and administer TPN as per ordered. Patient may have risk for nutrition imbalance.
3. Daily weight monitoring.
4. Monitor intake and output.
5. GI assessment eg. Frequency of bowel movement have to check and also bowel sound.
6. Patient have to advise to avoid food with high fiber , dairy products, spicy food fatty food .
7. Consume high protiens.



No comments:
Post a Comment